Regenerative medicine clinical trials continue to rise
Regenerative medicine, such as stem cell therapy, is the development and application of new treatments to replace or regenerate human tissue, cells or organs to establish normal function. As technology advancement continues to grow each year, so does the usage of these techniques. For example, 3D printing has created a new direction in biomanufacturing for tissue engineering. There are currently more than 1,500 regenerative medicine clinical trials in GlobalData’s Pharma Intelligence Centre, with this number rising every year.
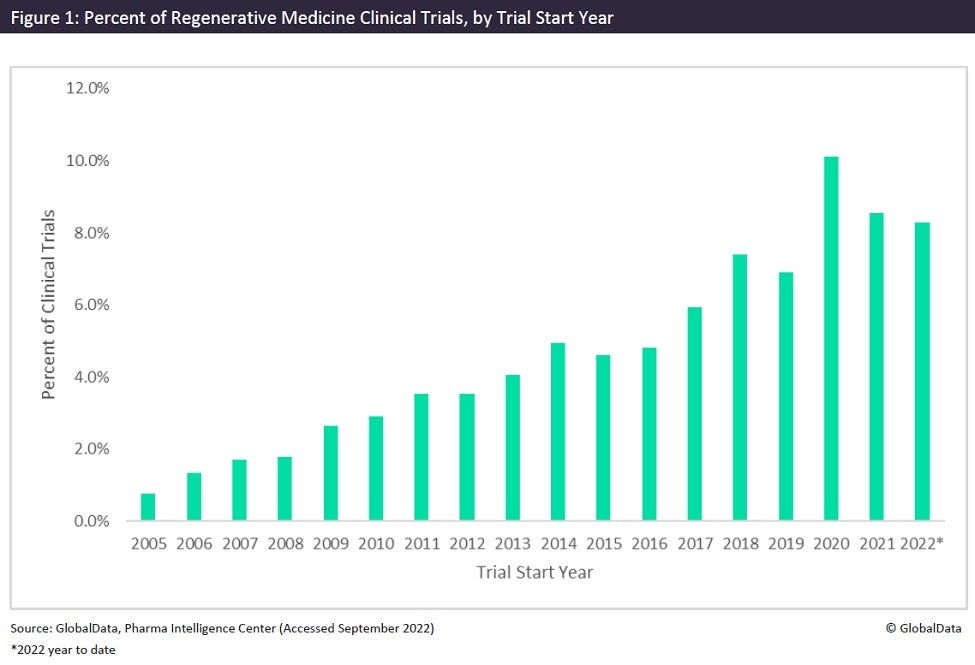
Overall, the number of regenerative medicine clinical trials increased from 2005 to 2018, with the most in 2020 at 10.1% of trials (Figure 1). 2020 was a key year for this practice due to several factors. According to the Alliance for Regenerative Medicine’s (ARM) 2020 annual report, these factors included the highest funding year, which raised a record $19.9bn, and an increase of 100 regenerative medicine developers from the previous year.
Two new therapies were also approved in 2020: Orchard Therapeutics’ Libmeldy, a gene therapy for the treatment of metachromatic leukodystrophy, received approval from the European Medicines Agency (EMA), while Kite’s Tecartus, the first CAR-T for the treatment of relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval.
The increasing number of regenerative medicine trials annually and the greater number of therapeutic drug approvals suggest that the practice will continue to be key in future drug development.
Related Companies
Experic
Ika-Werke
No Byline Policy
Editorial Guidelines
Corrections Policy
Source



